What is Economics?
- Social science - A study of people in society and how the interact with each other
- Study of rational systems
- Study of choices leading to the best possible outcome
Opportunity costs: The next best alternative which is foregone, when an economic decision is made. It is what you give up in order to have something else.
Scarcity: Not enough to around. This forces you to make decisions on what to keep.
Needs vs Wants: Needs are what is necessary to survive while wants are what is desired but not necessary for survival.
Ceteris Paribus: This is Latin for "Other things equal"
Economic Models: Economists create models to test and illustrate their theories and to make predictions.
The basic economic problem
Economics is the study of how scarce resources are allocated to fill the wants and needs of consumers.
Other basic economic problems
- What and how much of it should be produced
- How should it be produced.
- What kind of people should it be produced for?
These questions help allocate the resources.
Utility
The amount of usefulness or pleasure a product can give to a consumer
Total utility: Total satisfaction gained form consuming a total quantity of a product.
Marginal utility: Extra utility gained from each extra consumption of a product
Economic production
Factors of production
These are resources which allow an economy to produce output
- Land - Anything on, under or in land. Also raw materials.
- Labor - These are the workers
- Capital
- Physical - the stock of machinery and other things which produce stuff
- Human - the collection of skills
- Management - These are the people who organise the other factors of production and those who take risk to make profit.
Examples of factors of production
| Factors |
Teaching |
Car manafacturing |
| Land |
- Raw materials for equipment
- Land which school is built on.
|
- Raw materials for factory (Concrete, metal, glass,rubber)
- Land for factory
|
| Labor |
- Teachers
- Students
- Non-teaching staff
|
- Engineers
- Staff
- Factory workers
|
| Capital |
- Skills of staff
- Equipment
- School building
- Buses
|
- Equipment
- Skills of workers
- Factory building
|
| Management |
- Head of departments
- Organiser of buses
|
|
Production possibility curves
This shows the maximum combination of goods which can be produced by an economy In a given time period.
This assumes that:
- All resources are used fully and efficiently
- The current state of technology doesn't change
Production possibility curve diagram
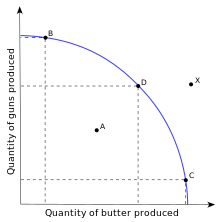
A point on the curve - The resources are allocated at maximum efficiency. E.g D
A point inside the curve - The resources are allocated inefficiently. E.g A
A point outside the curve - This allocation of resources is not possible E.g x
Straight line PPC significance: Opportunity costs are constant as products use same resources.
Curved line PPC significance: Opportunity costs vary. Products use different resources. The flat parts of graph indicate low opportunity costs while steep parts have high opportunity costs.
Macroeconomics Vs. Microeconomics
Macroeconomics
Economy in general.
- Interaction between inflation
- Unemployment
- Distribution of income
Microeconomics
The response and decisions of individuals in the economy.
- Reaction of quantity to changing price of product
- Theory of the firm
- Market structures
Positive economics: Can be proven by fact.
Normative economics: Matter of opinion.
Economic growth and development
Economic growth
National Income: Measured by value of output goods and services, or expenditure on the goods and services, or to the income of households.
Real National income: National income but with inflation taken into account.
Real national income per capita: The income per person. How this changes across a period of time, indicates economic growth.
Why doesn't economic growth indicate welfare?
The problem with economic growth is it only shows monetary growth and does not tell use about the actual increase in welfare of people. The country may grow but this growth may be going into luxury goods not necessity goods.

Economic development
The measurement of welfare growth in a state.
How is economic development measured?
- Education indicators
- Health indicators
- Social indicators
Human development indicators
This takes into account:
- Real national income per head
- adult literacy Rate
- Average years of schooling
- Life expectancy
It is mapped to a value between 0 and 1
Sustainable development
This is development which meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
For example:
- Not polluting planet by burning fossil fuels
- Planting trees after cutting them
- Using renewable energy sources.
Market systems
Market system Model

The market system model shows their are two markets, the resource market and product market and these exchange either goods and services, factors of production, or resources for money.
Rationing systems: planned vs free market
This is how scarce resources are rationed for the goods and services provided.
Planned economy: the government decides everything in the economy
Free market: The firms determine based on consumers wants how much to produce. Supply and demand determine price.
View count: 6676